Leveraging Schema Markup for Effective Semantic SEO.
Using Schema Markup for Effective Semantic SEO.
SEO is not just about keywords and links. It also involves how you present your content and structure your website. To achieve this, you can leverage schema markup, which consists of special snippets of code that describe your webpage content according to the markup standard.
What is Schema Markup and Why Is It Important for SEO?
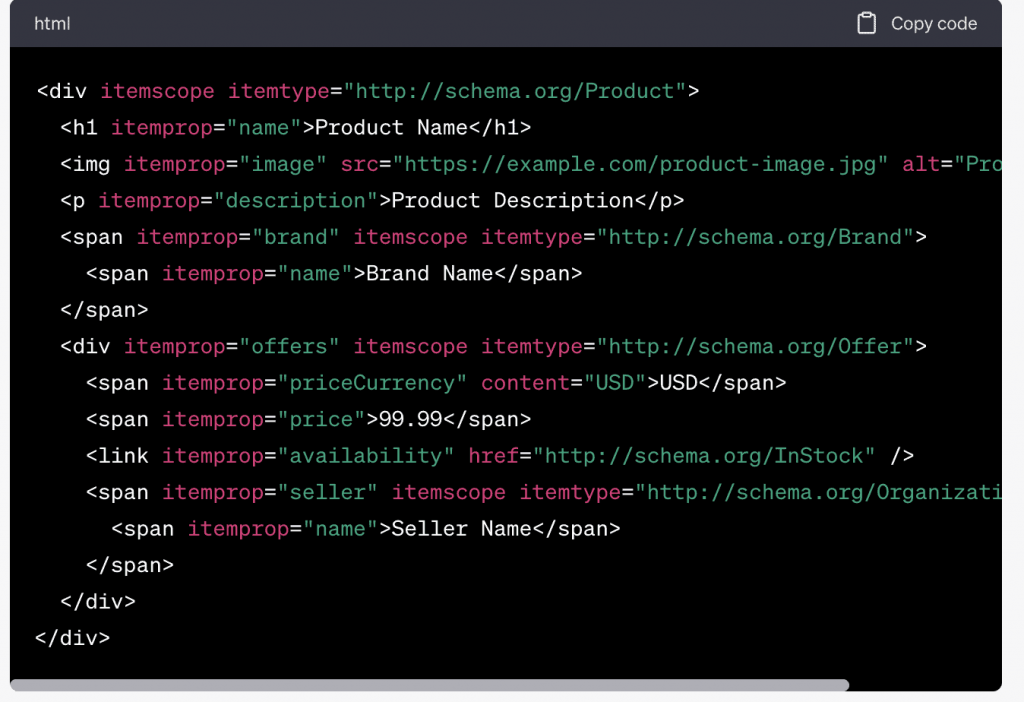
Schema markup, also known as schema.org markup or structured data markup, is one of standardized language used by major search engines and social media sites, including Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex. It uses specific tags or snippets of code added to HTML to provide additional context about the content on a webpage. These additional pieces of information help search engines understand the meaning and intent of the content, resulting in more relevant and enhanced search results.
The purpose of schema markup is to improve how search engines index and display information in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages). By adding structured data markup to your website, you essentially provide search engines with a blueprint of your content, making it easier for them to understand, identify and highlight important elements. This can include information such as product details, event dates, reviews, ratings, and more.
Functions of Schema Markup in Content Optimization.
They help search engines better understand the content and structure of a webpage, which can improve its ranking and relevance to user queries.
Adding structured data to your web pages enables them to show rich snippets in search results, which offer extra details to searching person about your webpage, such as ratings, prices, availability, duration, and more. These improved snippets can boost the appeal and click-through rate of a webpage, resulting in more engagement.
Structured data helps search engines to produce better answers to user questions, such as “Who is the author of the Harry Potter book?” or “How long does a flight from Warsaw to London take?”, as this data is easy to process from structured format. By using specific annotations, search engines can more easily distinguish between different meanings of the same word, such as “berry” (fruit or name) or “ball” (sports equipment or toy). These tags allow for precise understanding of context and more accurate matching of search results to user intent. They support also local optimization by helping search engines better understand the location and scope of a business, which can improve its ranking and relevance to user queries related to a specific place. It also enables the display of Google My Business listings, Google Maps, and other visual elements in search results, which include additional information about the business. It facilitates the creation of better answers to user questions, such as “Where is the nearest hairdresser?” or “What is the best restaurant in the city center?”.
Therefore, schema markup is an important tool for local SEO that can benefit both search engines and users.

Benefits of Adding Semantic Markup to Content.
Enhanced understanding of content by search engine bots. Search engines utilize bots that crawl website content to understand its context and topics. Adding semantic markup helps these bots better comprehend the page structure and find important information, which can lead to improved indexing and display in search results.
Increased click-through rates. Displaying more enriched results in search engines can attract greater user attention and increase click-through rates (CTR). If your results include additional information such as ratings or local data, it may entice users to click and visit your website.
Support for voice assistants and IoT devices. Voice assistants such as Siri, Google Assistant and Alexa use schema tag data to answer user queries. By adding schema tags, you can improve your visibility in voice search results and increase your chances of getting a voice response.
Enhanced display on social media platforms. Some social media platforms such as Facebook, Pinterest, and LinkedIn utilize schema markup to better understand content and display information such as titles, descriptions, images, etc. By incorporating pertinent structured data markup, you can govern how your content is showcased on these platforms.
Streamlined data processing. Schema tags make it easier for programs and tools to process data. You can use schema tags to define information such as ratings, reviews, product data, etc. This makes it easy for different systems to process this information automatically.
Increased conversions and sales. SEO tags can also help increase website conversions and sales as they can influence the purchasing decisions of users. For example, they can display customer reviews of a product or service, compare competitors’ prices or offers, show product availability or service lead times, provide contact information or business location, and more.
Building authority and credibility. Schema tags can also help build a site’s authority and credibility by showing search engines and users that the site is professional and updated. For example, displaying the date an article was published or updated, the number of citations or external references, the number of comments, likes or awards and certificates received by the site or its author.
Types of Schema.
Schema markup can describe different types of data and content on web pages, such as videos, articles, products, reviews, events, and more, and help search engines better understand and present this data in search results.
Here are a few different types of schema available on Schema.org:
Types of Places: restaurants, stadiums, airports, countries, cities, parks, museums, etc. These markup types allow for providing information about addresses, opening hours, ratings, reviews, etc.
Types of Businesses: dentists, hotels, legal services, real estate agents, etc. These allow for providing information such as business name, phone number, address, working hours, ratings.
Types of Products: books, music albums, clothing, vehicles, software, food, etc. These can be used to provide information about product names, descriptions, prices, availability.
Types of Events: concerts, festivals, sports events, exhibitions, workshops, webinars. These allow for providing information about event names, venues, dates, times, tickets.
Types of Articles: news articles, blog posts, scientific articles, etc. These can be used to provide information such as article titles, authors, publication dates, related posts.
Types of Reviews: these allow for providing information about product or service ratings and user comments.
The above examples are just a few of the many types of markup available on Schema.org. There are many other types of markup that can be used depending on the specific context of the website and the information one wants to convey.
Microdata, RDFa, JSON-LD.
What are microdata?
Microdata schema tags are special code snippets that can be added to a website to provide search engines with more detailed information about its content. Imagine a website as a book, and microdata tags as a kind of table of contents that helps search engines understand what the website is about.
Difference between microdata and schema markup.
Semantic markup and microdata in text are related but not the same. They are two different ways of structuring information that can be used to make content easier to find and understand.
Schema markup uses standard markup (such as JSON-LD, RDFa, Microdata) to describe content such as products, reviews, events, articles, etc. This allows search engines to better understand the content and display more detailed search results.
This can be compared to language and grammar. Schema markup is like a language that has specific words and meanings. Microdata is like a grammar that specifies how these words are to be used and arranged.
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) and JSON-LD (JSON for Linked Data) are two different ways of adding structured metadata to web content.
RDFa can be compared to a hidden message embedded in the source code of a website. It’s like a hidden message that is only accessible to special “eyes.” With RDFa, we can add web content information such as title, description, author, classifications, etc. without changing the content visible to users.
It’s like magically embedding additional information in the background of a web page that is only understood by search engines and data analysis tools.
JSON-LD
On the other hand, JSON-LD is a more modern way of adding structure to web content. It’s akin to adding labels to individual content elements so that search engines can easily read them. JSON-LD uses the human-readable JSON data format, which is popular in programming. This allows us to precisely define various content elements, such as name, date, description, geographic location and more. These labels help search engines understand the structure of the content and index it better.

